(Only available in Portuguese)
By Winfridus Overbeek. Movimento dos Pequenos Agricultores (MPA) do estado do Espírito Santo, with the support of the WRM
Um alerta sobre o Fomento Florestal: experiências...e alternativas
Large-Scale Tree Plantations
Industrial tree plantations are large-scale, intensively managed, even-aged monocultures, involving vast areas of fertile land under the control of plantation companies. Management of plantations involves the use of huge amounts of water as well as agrochemicals—which harm humans, and plants and animals in the plantations and surrounding areas.
Other information
22 January 2009
Multimedia
29 December 2008
Since its invention paper has been a vehicle for education and an essential tool for communicating our thoughts, ideas, dreams and beliefs. Paper is associated with images of education, access to written information and a better quality of life. Yet there are many problems caused by the way we consume and produce paper.
Publications
22 December 2008
(Only available in French)
Populations locales versus plantations commerciales d’hévéas et de palmiers à huile dans le Sud-Cameroun
By Julien-François Gerber
Résistances contre deux géants industriels en forêt tropicale
Publications
18 December 2008
By Chris Lang
Publications
15 December 2008
Eucalyptus, oil palm, rubber and jatropha monoculture plantations are expanding onto local communities’ lands and forests in the Mekong region’s countries. Promoted under the guise of development, poverty alleviation and even climate change mitigation, such plantations are resulting in severe social and environmental impacts.
Publications
15 December 2008
Timber plantations in southern Africa are concentrated in South Africa, Zimbabwe and Swaziland, but they are also expanding in Mozambique. There are smaller areas in Angola, Zambia, Malawi and Tanzania. In South Africa, the largest areas are in the provinces of Mpumalanga, KwaZulu-Natal and the Eastern Cape, covering 1.5 million hectares of land. Additionally, an estimated 1.6 million hectares have been invaded by plantation species such as acacias (wattle), eucalyptus (gum) and pines.
Publications
15 December 2008
Oil palm and rubber plantations occupy extensive areas in many countries in tropical Africa. In spite of their social and environmental impacts, until now they have received scant attention both at the national and international level.
Publications
15 December 2008
Switching from fossil to alternative liquid fuels would appear to be a good idea, particularly in the context of climate change. Such is the case of converting the cellulose contained in plants into different types of fuels, among which liquid ethanol, that could be used in transport as an alternative to gasoline. However, current developments in this field show a number of threats that need to be highlighted.
Bulletin articles
15 December 2008
Welcome to the Mekong region!
Bulletin articles
15 December 2008
The inter-meshing of the six economies in the Mekong Basin since the 1990s has been fostered under the Greater Mekong Sub-region economic cooperation programme. This was aimed at increasing the flow of cross-border investment from countries with considerable economic might such as China, Thailand and Vietnam into neighbouring countries such as Laos PDR and Cambodia, which have a ‘doors wide open’ approach calling for foreign companies to come to invest.
Other information
15 December 2008
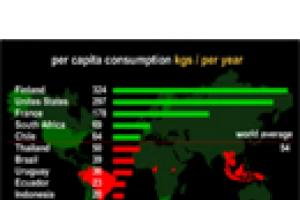
China’s growing pulp and paper market is being the world's fastest. Although per capita paper consumption is less than ten per cent of the amount consumed in the US, China accounts for 14 per cent of global paper consumption. Jaakko Pöyry has estimated that paper consumption in China would increase at 4.4 per cent a year between 2000 and 2015. Much of that “consumption” is used in packaging of goods for export, which means that real per capita paper consumption in China is actually much lower.
Other information
15 December 2008
Investments by foreign companies in commercial tree plantations in Laos PDR increased sharply increased during 2004-2006. Large scale plantations are promoted through state land concessions. Currently, an area of 167,000 ha has been transferred to foreign companies under large scale land concessions in the central and south regions of Laos. Of these, 48% or 80,000 ha are dedicated to rubber, and 28% of 46,600 ha are allocated to growing eucalyptus. However, the total area for growing rubber throughout the country has increased to 182,900 ha.